Investing in stocks is one of the wealth building vehicles. Real estate and business are the other two ways to build wealth. There are many components to investing but it does not have to be complicated. You can grow your money simply by investing in index funds.
Stock
A stock (shares or equity) is a type of investment that represents an ownership in the company. Corporations sell stocks to raise funds to operate their business. If a company issues 1,000 shares and you own 100 shares, you would therefore own 10% of the company’s assets and earnings.
Mutual Fund
Mutual fund is a financial vehicle made up of a pool of money collected from many clients to invest in stocks, bonds or other assets. Professional money managers operate these funds. Buying mutual funds gives individual investors the ability to own a diversified portfolio for a fraction of a cost than buying individual shares. If you have money in an employer-sponsored retirement plan, the chances are certain you own mutual funds.
ETF
Exchange-traded fund (ETF) is also a form of pooled fund investing. In contrast, the difference is that ETFs are traded throughout the trading day while the mutual funds trades close at the end of the trading day. Most noteworthy is that ETFs have lower fees since they are passively managed while the mutual funds are actively managed. This means there is no sales charge or commission (no loads) associated with the ETFs. These are the reasons why these funds that began trading in the 1990’s are becoming more popular with investors.
Small, Mid, and Large Caps
Small-Cap company is a company whose market capitalization (shares x value of each share) is between $300 million and $2 billion.
Mid cap stocks are shares of companies with market capitalizations between $2 billion and $10 billion.
Large-cap stocks are shares of a company with a market capitalization of more than $10 billion. They are also referred to as blue chip stocks. Well-known companies such as Microsoft, Apple, Johnson & Johnson and Walmart are some examples of large cap companies.
Growth and Risk
Small cap stocks have the potential to grow therefore can offer larger returns faster. Because of this it is considered riskier and has more volatility. The large cap stocks provide safer returns but not always. There are plenty of big companies that collapsed. Enron, Blockbuster, and Kodak are examples. For these reasons, it’s important to diversify your portfolio with small, mid, and large cap stocks. Investing in the long term can also minimize your risk.
Bond
A bond is a loan made by an investor (you) to a borrower (corporate or government). Therefore, when you purchase bonds, you become a lender. Bonds have an end date when the principal of the loan is due. The prices of bonds are inversely correlated with interest rates. This means when the interest rates go up, bond prices fall. Municipal bonds are bonds, that are exempt from federal taxes and often state taxes and can help investors who are in a high tax bracket.
Ratio of Stocks to Bonds
The old rule of thumb was that you should subtract your age from 100 and that’s the percentage that you should keep in stocks. For example, if you’re 40, you should keep 60% in stocks. Due to the reason that people are living longer and spending longer time in retirement, the new rule is to subtract from 110 or 120.
Here is an example of a diversified portfolio:
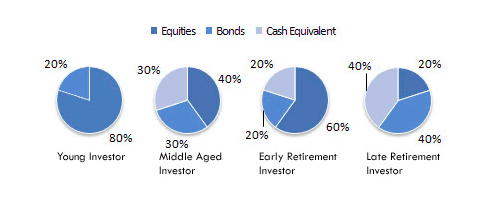
Index Fund
An Index fund is a type of a mutual fund that tracks a financial market index. The popular Standard & Poor’s 500 Index, represents 500 largest companies in the U.S. Investing in an index fund is a way of owning many stocks at a low cost. The legendary Warren Buffet recommends index funds for average investors.
Low Cost
One of the best reason for investing in the index fund is the low cost. The average expense ratio for index funds are 0.09% versus 0.82% for actively managed mutual funds. Higher cost does not result in better performance. In fact, 90% of index funds earned a higher return than the managed mutual funds. When you don’t have to pay a fund manager, you get to keep more money therefore your investment can grow faster. In general, invest in funds with an expense ratio of 0.20% or less.
Furthermore, index funds have a low turnover rate. Each time a stock is sold, capital gains taxes must be paid and consequently results in higher cost. Reducing the turnover further adds to the low cost of the index funds.
Type of Index Funds
There are many asset classes so there are many index funds that track specific sectors. Standard & Poor’s 500 Index is the most popular. Other funds include the broad market, international, and bond funds.
Broad Market
Broad market index funds hold securities in and more than 3,000 companies, whereas the S&P 500 index fund has 500 company shares. Here are some broad market index funds:
- Vanguard Total Stock Market Index Fund ETF Shares (VTI)
- Schwab Total Stock Market Index Fund (SWTSX)
- Schwab U.S. Broad Market ETF (SCHB)
S&P 500
Standard & Poor’s 500 index fund invests in 500 large-cap U.S. companies. you own equities in 80% of U.S. equity.
- Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO)
- Schwab S&P 500 Index Fund (SWPPX)
- Fidelity Spartan 500 Index Investors Shares (FUSEX)
Market Capitalization
These funds track small and mid-sized companies:
- Vanguard 500 Index Fund (VFIAX, VOO) tracks the S&P 500 Index, which are the 500 largest U.S. companies by market cap
- Fidelity Mid Cap Index Fund (FSMDX) tracks the Russell Midcap Index
- iShares Morningstar Small-Cap (JKJ) tracks the Morningstar Small Core Index
International
Some international index funds track the foreign market in developed countries in Europe, Australasia and Far East (EAFE). And there are funds that track the market in emerging markets such as Brazil, Russia, India and China, also known as BRIC countries.
- Vanguard FTSE All-World ex-US Index Fund ETF Shares (VEU)
- Schwab Emerging Markets Equity ETF (SCHE)
- Fidelity China Region Fund (FHKCX)
Bond
There are specific bond funds that tracks short-term, intermediate or long term, based on when they mature. Alternatively, you can purchase a bond fund that has a mix of all of the bonds.
- Vanguard Total Bond Market Index (VBMFX)
- Vanguard Long-Term Bond Index Fund (VBLAX, BLV)
- iShares Intermediate Government/Credit Bond ETF (GVI)
- Fidelity Short-Term Bond Index Fund (FNSOX)
Sector
There are other sectors such as utilities, real estate, and information technology, i.e. cloud management, that should not be ignored.
- iShares U.S. Financials ETF (IYF) tracks the Dow Jones U.S. Financials Index
- Utilities Selector Sector SPDR Fund (XLU) tracks the Utilities Select Sector Index
- First Trust Cloud Computing ETF (SKYY) tracks the ISE Cloud Computing Index
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is an investment strategy to balance risk and gain by splitting your money into buckets of stocks, bonds, and cash. You can build a balanced portfolio by investing in several types of index funds that track different indexes. For example, you can put 65% of your money in stock funds, 30% in bond index funds, and 5% in cash or cash equivalence.
Brokerage Firms
Before you can invest in index funds, you first need to open a brokerage account. You can buy, sell, and trade index funds, mutual funds, and stocks through these brokers. I look for ease of use and the ability to talk to a live person when choosing a broker. Here are my favorites:
Putting It All Together
You can adjust the allocation depending on your risk tolerance, age, and other sources of income and retirement status. The most important thing is to get started in building your nest egg in paper asset.
Here’s an example of allocating $10,000 into 6 different index funds.
Assets | Percent
| Ticker Symbol | Allocation of $10,000 |
Domestic stocks | 45% | 25% large cap: VTI | $4500 |
10% mid cap: FSMDX | $1500 | ||
10% small cap: JKJ | $1500 | ||
International stocks | 15% | VEU | $1500 |
Other | 5% | XLU | $500 |
Bonds | 30% | VBLAX | $3000 |
Cash | 5% | Money market or CD | $500 |
“The Stock Market is designed to transfer money from the Active to the Patient.”
“Someone’s sitting in the shade today because someone planted a tree a long time ago.”
Warren Buffett
